What is Meniere's disease and who can it affect?
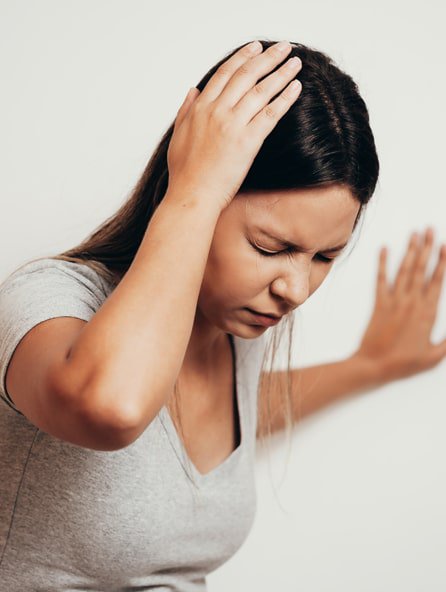
Meniere’s disease is a pathology that affects the middle ear that generates vertigo, hearing loss (decreased hearing) and tinnitus (ringing in the ear). In most cases, it affects only one ear, although it can be bilateral in a small percentage of cases.
In most cases, the clinical presentation begins with tinnitus or hearing loss followed by intense vertigo that can last from minutes to hours. Meniere’s disease can occur at any age, but is more common after 40 years of age.
There are many theories as to why people get Meniere’s disease but there is no definitive cause.
Some researchers believe that it is due to the constriction of blood vessels similar to what occurs in migraines, others due to autoimmune reactions, viruses or allergies or even genetic variations.

Who diagnoses and treats Meniere’s disease is the otorhinolaryngologist who is the specialist in ear, nose and throat.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical history that the patient refers to the specialist and the presence of:
-Two or more episodes of vertigo lasting at least 20 minutes each
-Tinnitus
-Temporary hearing loss
-Sensation of covered or full ear
Audiometry is required to confirm hearing loss and recovery after the crisis.
The treatment will depend on each patient, the symptoms and their intensity, ranging from drug treatment, low sodium diet (low salt), changes in diet, cognitive therapy, intratympanic injections (inside the ear) and surgery.
The vast majority of patients are controlled with diet and medical treatment, the small percentage in whom control is not achieved in this way is subjected to surgery or more invasive treatments to control vertigo that becomes disabling.
There is no cure, only the control of the disease given through medication or surgery, always by the otolaryngologist.
No existe una cura solo el control de la enfermedad dado a través dDe medicamentos o cirugía siempre por el otorrinolaringólogo.